The search engines like Google, Yahoo, Bing, etc. have a vast playground with immense databases and companies are playing hard to stand first in the same search engine database.
To accomplish it, SEO is a good practice to be followed these days. Seo is the process of getting the traffic from the free, organic, editorial or natural search results on search engines. Search Engine Optimisation (SEO) in 2018 is a technical, analytical, and creative process to improve the visibility of a website in search engines. The primary function of SEO is to drive more unpaid useful traffic to a site that converts into sales.
Though, it is constantly inviting changes in its practice. All major search engines have primary search results, where web pages and other content such as videos or local listings are shown and ranked based on what the search engine considers most relevant to users.
As an SEO practitioner, you need to understand that there is no magic way to rank your website on the first page of Google. Search engines are governed by complex algorithms and it takes a lot of time and effort to ‘convince’ them that your website or web page deserves one of the top spots.
There are certain rules that one should follow to optimize the website to provide the search engine with the necessary signals. Almost every day, Google introduces changes to its ranking algorithm. Some are tiny tweaks; others seriously shake up the Search Engine Result Pages (SERPs). Let’s find out what the updates are in years (descending) to have an overview of the changes in the ranking algorithm.
2018 Updates:
Core Update- Rank Risk Index (Google SERP Fluctuations)
Confirmed date: March 09, 2018.
Hazards: SERP Fluctuations and ranking
About the update:
Rank Risk Index is one of the tools in Google algorithm monitoring service that helps to measure SERP fluctuations for the “N” number of domains and keywords.
While sharing the update, Google confirmed that they ran a broad core algorithm update where they explained what exactly means if page drops could impact the appearance and rankings of some websites in the search results or not.
Rank Risk Index during the update testing began recording increased rank fluctuations on both desktop and mobile. While the uptick in rank fluctuations was initially moderate, the Rank Risk index caught an unusual and highly significant upsurge. According to the index, fluctuations reached a level of 99 – out of 100 on desktop and 92- out of 100 on mobile.
Page Speed to Become Mobile Ranking Factor
Confirmed date: JANUARY 18, 2018
Hazards: Page ranking
About the Update:
Since 2010, Page speed has been a ranking factor on desktop and Google announced that page speed would become a mobile ranking factor in January. However, with this announcement, it becomes official that the ranking factor now is an official part of a mobile page’s placement on the Google SERP come July 2018.
Rest confirmation would be given once updates related to slow-loading pages will be targeted. As such, the search engine does not predict that an extensive number of pages will be impacted as the ranking factor becomes incorporated into the algorithm this July. According to Google, the pending mobile page speed ranking factor exists independently of the mobile-first index.
Snippet Length Increase —
Confirmed Date: November 30, 2017
Hazards: Snippet Description Length
About the update:
A snippet is the content description of a page shown below the URL in an organic search result that helps to show how it relates to the search query which is often dynamically generated based on the user query and content found in both the meta description and the content visible on the page.
Earlier Google always recommended adding a description to a snippet between 50-150 words to give an overview of the search query, however, you can write a snippet of any length but won’t give a benefit as per SEO guidelines. While testing for snippets over two years,
Google realized in 10K tracking data for December 15th, which consisted of 89,909 page-one organic results, the average display snippet (stripped of HTML, of course) was 215 characters long well above historical trends. This led Google to adopt a new Meta Description limit up to 300 characters from the previous 155 (almost doubling).
Chrome HTTPS Warnings —
Confirmed Date: October 17, 2017
Hazards: Chrome Communication and data security
About the update:
Google has always been looking for ways to improve how Chrome communicates the connection security of HTTP pages. You must have noticed after the update that Chrome now marks HTTP pages as “Not secure” if they have password or credit card fields.
Under these two additional situations, Chrome shows the “Not secure” warning:
- when users enter data on an HTTP page
- all HTTP pages visited in Incognito mode
Based on increasingly broad criteria, HTTP sites as non-secure is taking place in gradual steps. Any type of data that users type including passwords and credit cards into websites should not be accessible to others on the network.
There has been a 23% reduction in the fraction of navigations to HTTP pages with password or credit card forms since the change in Chrome 56, on the desktop. Therefore, since the update, whenever the user types data into HTTP sites, the Chrome 62 version will show the “Not Secure” warning. With the same discovery, Google started warning visitors to sites with unsecured forms. This has been an important step in Google’s push toward HTTPS though it’s not an algorithm update but may have a material impact on site traffic.
Google Jobs —
Confirmed Date: June 20, 2017
Hazards: Duplicate Jobs
About the Update:
Google has launched a new jobs search feature in June 2017 which shows right on its search result pages that let Google users search for jobs across virtually all of the major online job boards like LinkedIn, Monster, DirectEmployers, CareerBuilder and Facebook and others.
The idea here is to give job seekers an easy experience and way to see which type of jobs are available without having to go to multiple sites only to find duplicate postings and lots of irrelevant jobs.
To create this comprehensive list, Google first has been removing all of the duplicate listings that employers post to all of these job sites. Then, its machine learning-trained algorithms sift through and categorize them. These job sites often already use at least some job-specific markup to help search engines understand the criteria of the job posting.
Intrusive Interstitial Penalty —
Confirmed Date: January 10, 2017
Hazards: User experience, unnecessary pop-ups
About the Update:
An Intrusive Interstitial is an activity of showing a popup or alert that covers the main content, either immediately after the user navigates to a page from the search results, especially on mobile phones, or while they are looking through the page. It’s a kind of displaying a standalone interstitial that the Google user has to dismiss before accessing the main content.
Google officially announced on January 10, 2017, that it would begin cracking down on intrusive interstitials. The agenda behind this is that this type of ad or popups can be problematic and give a pathetic user experience, especially on mobile devices where screens are often smaller and can hamper the user experience.
Google will be potentially penalized as this is also lowering the rankings of web pages. During the update, Google said these pages where content is not easily accessible to a user on the transition from the mobile search due to intrusive interstitials, results may not rank as highly. Although, Google also provided a rare warning of this update five months in advance.
Fred
Confirmed Date: March 8, 2017
Hazards: high-quality post or content, misguiding guidelines for showing ads
About the update:
Fred isn’t really an algorithm or even one set of processes. It is a catchall name for any quality related algorithm updates related to site quality that Google does not otherwise identify. Fred targets websites that violate Google’s webmaster guidelines.
The majority of affected sites are blogs with low-quality posts that appear to be created mostly for the purpose of generating ad revenue. You need to make sure that your pages on the website have high-quality and relevant information if you have registered the website for showing ads. Don’t try to trick Google into thinking your page is about something as Google can analyze easily about the page or site that is the full gateway to affiliate links.
2016 Updates
Penguin 4.0, Phase 1 & Penguin 4.0 Announcement —
Confirmed Date – September 27, 2016, & September 23, 2016
Hazards: spamming
About the update:
Penguin is a real-time signal-processed – filter tool that is designed to capture sites that are spamming Google’s search results, within its core search algorithm which operates on a periodic base. This tool is helpful when Google’s regular spamming systems are not able to detect the spamming.
The new Penguin is baked into the core algorithm with small initial impact assessments which was later revealed that the Penguin 4.0 rollout was unusually long and multi-phase. Google’s algorithms generally rely on more than 200 unique signals or clues that make it possible to surface what you might be looking for.
These signals include things like the specific words that appear on websites, the freshness of content, your region and PageRank. One specific signal of the algorithms is called Penguin, which was first launched in 2012 and today has an update.
Mobile-friendly —
Confirmed date: May 12, 2016
Hazards: mobile friendly ranking
About the update:
Google’s mobile-friendly algorithm is a page-by-page signal as Google takes time to assess each page on the web no matter how fast Google crawls and indexes all pages of your site. The impact will be slow to show up. Just after the original mobile-friendly update, Google rolled out another update to boost the benefit of mobile-friendly sites on mobile search.
However, the impact of the latest update is small as the majority of sites are mobile-friendly. This technology is supposed to “increase the effect of the [mobile-friendly] ranking signal.”
AdWords Shake-up —
Confirmed Date: February 23, 2016
Hazards: spacing in Display AdWord Ads
About the update:
Earlier Google used to have 1-3 ads at the top of the ad block. Google has been testing SERPs with 4 ads at the top of the page and is rolling out a change to Google AdWords which lead to a ton of speculation in the PPC Community. The 4 ads seem to be at the top of the search results, none on the sidebar at all, and an additional 3 ads at the bottom of the search results. This replaces the usual mix of top, bottom, and sidebar-heavy AdWords ads, depending on the specific search result. While this was a paid search update, it had significant implications for CTR for both paid and organic results, especially on competitive keywords.
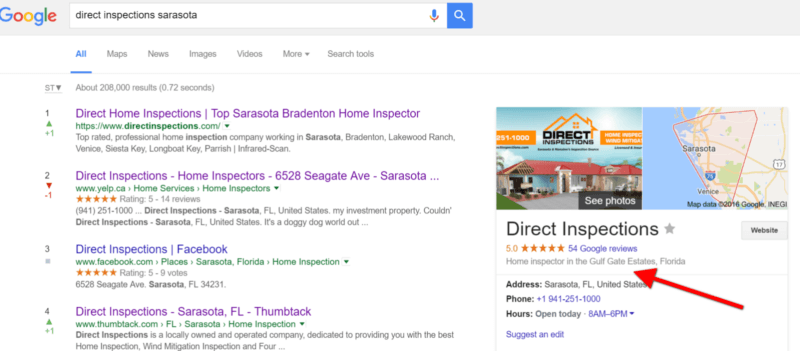
Possum
Confirmed Date: September 1, 2016
About the Update:
Possum is one of the updates that ensured that local results vary more depending on the user’s location, for example, the closer you are to a business’s address, the more likely you are to see it among local results. Possum also resulted in a greater variety of results ranking for very similar queries, like “Direct Inspections” and “Direct Inspections Co.”. Interestingly, Possum also gave a boost to businesses located outside the physical city area.
2015 Updates
RankBrain —
Confirmed Date: October 26, 2015
Hazards: Optimize content, best search results
About the update:
RankBrain is Google’s name for a machine-learning artificial intelligence system and part of Google’s Hummingbird algorithm that’s used to help process its search results which use artificial intelligence to filter results. It is one of the hundreds of signals that go into an algorithm that determines what results appear on a Google search page and where they are ranked.
It helps to find out the actual meaning and purpose behind queries and provide the best matching response to those queries. RankBrain is the third most important ranking factor in Google which helps to optimize content for relevance and comprehensiveness with the help of competitive analysis. It helps Optimize content for relevance and comprehensiveness with the help of competitive analysis.
Mobile Update AKA “Mobilegeddon” —
Confirmed Date: April 22, 2015
About the Update:
When it comes to searching on mobile devices, users should get the most relevant and timely results, no matter if the information lives on mobile-friendly web pages or apps. As more people use mobile devices to access the internet, algorithms have to adapt to these usage patterns. Mobilegeddon ensures that mobile-friendly pages rank at the top of the mobile search while pages not optimized for mobile are filtered out from the SERPs or seriously down-ranked.
Other Major Updates:
Panda
Confirmed Date: February 24, 2011
Hazards: Duplicate, plagiarized or thin content; user-generated
spam; keyword stuffing
Panda is a search filter introduced to stop sites with poor-quality content by assigning the so-called quality score to web pages; from working their way into Google’s top search results. This score is later used in deciding the ranking factor as well.
This tool helps to rectify duplicate or plagiarized content and excessive keyword stuffing. Initially, Panda was a filter rather than part of Google’s ranking also, but in January 2016, it was officially incorporated into the core algorithm. Panda rollouts have become more frequent, so both penalties and recoveries now happen faster.
Hummingbird
Confirmed Date: August 22, 2013
Hazards: Keyword stuffing; low-quality content
Hummingbird is a search algorithm used by Google to improve results for a conversational search, instead of just looking for keywords it helps the user search specific questions. It pays more attention to each word in a query, ensuring that the whole query the whole sentence or conversation or meaning is taken into account, rather than particular words. The goal is to provide the right search result that matches the meaning to search than pages matching just a few words.
Pigeon
Confirmed Date: July 24, 2014 (US); December 22, 2014 (UK, Canada, Australia)
Hazards: Poor on- and off-page SEO
Pigeon stresses on searches which are based on location. The update created closer ties between the local algorithm and the core algorithm: traditional SEO factors are now used to rank local results. A good way to start with off-page SEO is getting listed in relevant business directories.
Google: Payday Update
Confirmed Date: June 11, 2013 –
The Payday Update was a new algorithm targeted at cleaning up search results for traditionally spammy queries such as pornographic and other heavily spammed queries.
Google: Pirate Update
Confirmed Date: August 2012
Pirate Update is a filter designed to prevent sites with many copyright infringement reports from ranking well in Google’s listings. The filter may also catch new sites that escaped being caught before, plus it may release false positives that were caught.
Google: EMD Update
Confirmed Date: September 2012
The EMD Update for Exact Match Domain – a filter Google launched to prevent poor quality sites from ranking from an irrelevant site. Earlier, Google used to rank those sites on top who had words that match the search terms in their domain names which led to many fluctuations and irrelevancy in ranking. Since the update has come into functioning, the sites have improved their content and ranking.
I hope the list of updates give you an idea how Google keeps on updating each second just to give a better user experience.